Interferometer | Ultra-precise length and angle measurement
- Details
- Hits: 13319
For high-precision position, angle or other measurement Distance measurement are suitable interferometer excellent because, based on the superposition of waves, they meet the requirements for extreme precision, for example in production measurement technology, Research or space travel. In this article we will introduce you to some new products from different manufacturers and give you a little basic knowledge.

Contents
Interferometer 2024 – The most important things in brief
Modern interferometers use advanced Laser technologies with stable, variable or femtosecond lasers. The algorithms for data analysis are also constantly being developed. The Fourier transform can be used to convert interference patterns into a frequency domain, which makes the analysis and interpretation of the data easier. Machine learning and KI are used to recognize patterns in the data and make predictions about material behavior or properties.
During the Research Interferometers measure molecular and atomic distances, providing crucial insights for materials science, biology and chemistry. In astronomy, interferometers are used to measure distances and movements of stars and galaxies with high accuracy. In nanotechnology, the precision measuring devices measure deformations and dimensions on the nanoscale, which is important for the development of nanomaterials and devices.
Interferometers can therefore measure distances, material deformations and optical properties extremely precisely and thus set new standards in measurement technology.
Interferometer for high-precision wafer thickness measurement
 19.01.2024/XNUMX/XNUMX | An important process step in the production of semiconductor wafers is the lapping of the silicon blanks, which are brought to a uniform thickness. For continuous thickness control Micro-Epsilon developed the white light interferometer IMS5420-TH. It opens up new perspectives in the industrial thickness measurement of monocrystalline silicon wafers.
19.01.2024/XNUMX/XNUMX | An important process step in the production of semiconductor wafers is the lapping of the silicon blanks, which are brought to a uniform thickness. For continuous thickness control Micro-Epsilon developed the white light interferometer IMS5420-TH. It opens up new perspectives in the industrial thickness measurement of monocrystalline silicon wafers.
Thanks to the broadband Superluminescent diode (SLED), the IMS5420-TH can be used for undoped, doped and highly doped SI wafers. The thickness measurement range is 0,05 to 1,05 mm. The measurable thickness of air gaps is even up to 4 mm.
The interferometers each consist of a compact Sensor and a Controller, which comes in a robust industrial grade Housing is accommodated. An active temperature control is integrated into the controller, which ensures high stability of the measurement.
The interferometer is available as a thickness or as Multipeak thickness gauge. The multipeak thickness measuring system measures a thickness of up to five layers such as wafer thickness, air gap, foil and coatings >50 µm. For thickness measurement under difficult environmental conditions, the IMS5420 controller was equipped with IP67 and a stainless steel housing - suitable light guides and sensors are available.
Interferometer for simultaneous length and angle measurement
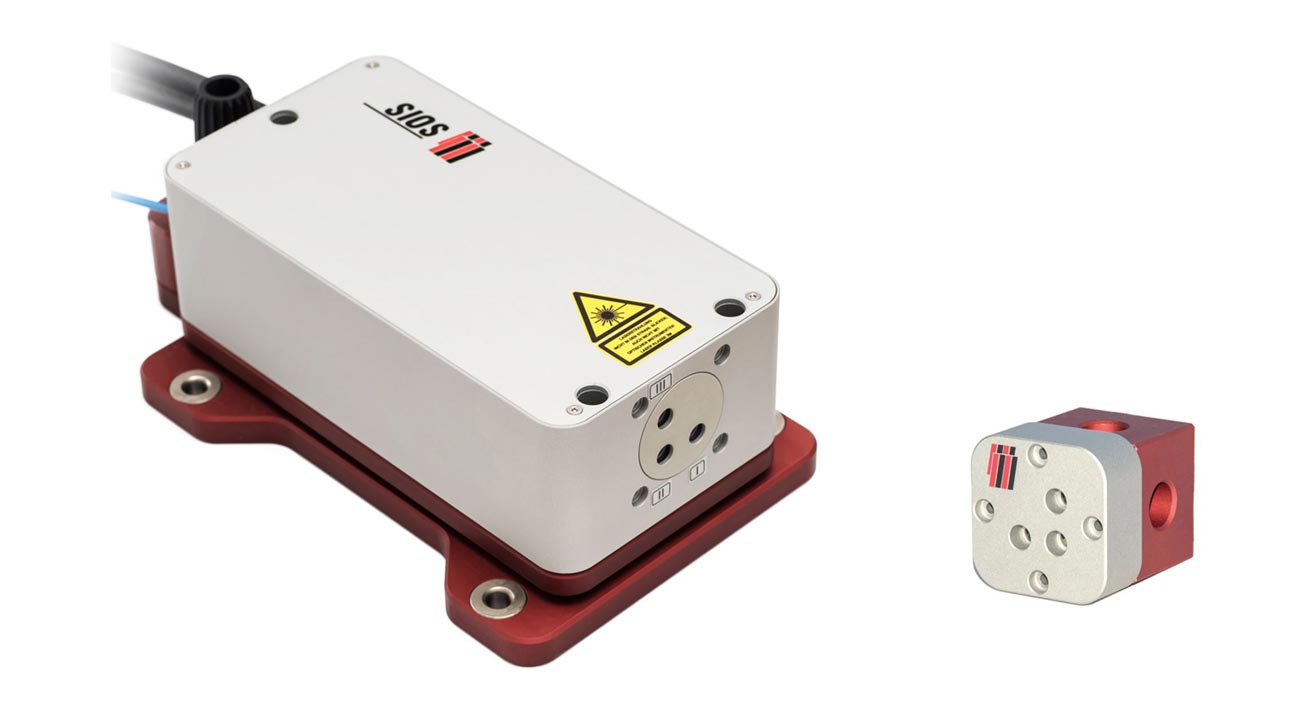
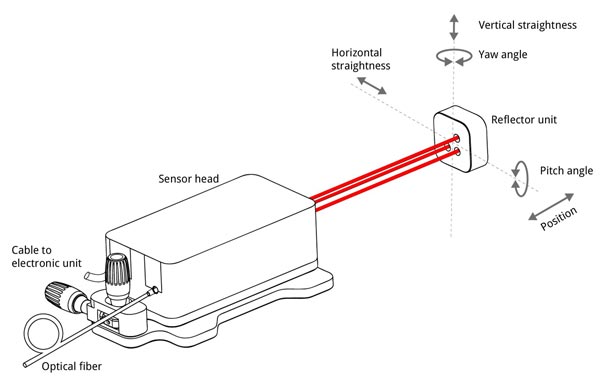 April 01.04.2020, 5000 | When it comes to high-precision simultaneous path and angle measurements in industry and research, quick setup and uncomplicated adjustment are particularly important. The three-beam laser interferometer SP XNUMX TR (picture above) from sios are precision length measuring devices that combine three interferometers in one device. The same highly stable laser frequency is used in all three measurement channels. Three length values are recorded simultaneously with nanometer precision. The corresponding angle can be determined with high precision from the difference between two length values and the calibrated beam distance.
April 01.04.2020, 5000 | When it comes to high-precision simultaneous path and angle measurements in industry and research, quick setup and uncomplicated adjustment are particularly important. The three-beam laser interferometer SP XNUMX TR (picture above) from sios are precision length measuring devices that combine three interferometers in one device. The same highly stable laser frequency is used in all three measurement channels. Three length values are recorded simultaneously with nanometer precision. The corresponding angle can be determined with high precision from the difference between two length values and the calibrated beam distance.
The modular three-beam interferometer can thus be adapted to a wide variety of measurement tasks. The distance measuring range is more than 5 m with one Sub-nanometer resolution. Angle measurements are possible up to ±12,5° with a reflector. The optical fiber coupling of the sensor head and the optionally integrated beam direction detection support easy handling and adjustment.
The new design of the interferometer is compact and robust. This makes it suitable for high-precision measurements in industry and research and as an OEM device. For large measuring ranges or calibration tasks, the manufacturer recommends using wireless temperature sensors or the LCS climate measuring station.
Interferometer with unprecedented accuracy
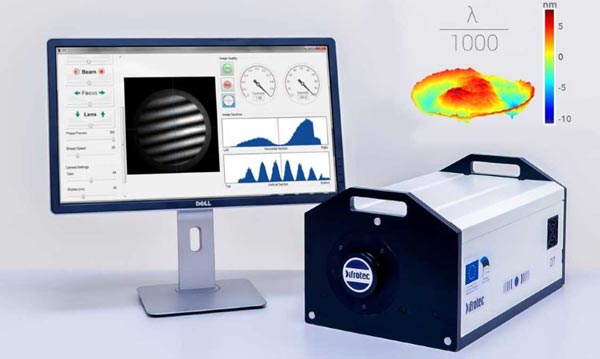 March 26.03.2020, XNUMX | Interferometry is the first choice optical measurement methodwhen it comes to measuring surfaces with high precision. Nortus Optronic now presents the new D7 interferometer from Difrotec with, according to its own information, unprecedented accuracy. The difference between measured and actual shape is less than lambda/1000 (< 0,6 nm).
March 26.03.2020, XNUMX | Interferometry is the first choice optical measurement methodwhen it comes to measuring surfaces with high precision. Nortus Optronic now presents the new D7 interferometer from Difrotec with, according to its own information, unprecedented accuracy. The difference between measured and actual shape is less than lambda/1000 (< 0,6 nm).
With the interferometer D7 we present a system that represents an innovative milestone in the field interferometric Measurement Technology represents. And so it offers an accuracy that sets standards in the field of interferometry, the compact, user-friendly interferometer.
Interferometer as a so-called PSPDI system (Phase Shifting Common Path Point Diffraction Interferometer): While the usual Fizeau interferometers require an optical reference, the D7 produces a perfect reference itself - a diffracted wavefront created by a sub-wavelength aperture in a thin metal film. The technology is patented in Europe and the USA.
The D7 is used to test high-precision optics with complex shapes and large aspherical deviations. The Difrometric software is supplied with the system. Due to the wide range of functions, the software offers a perfect analysis of the measurement results.
FAQ
What does an interferometer do?
An interferometer is a precise measuring instrument, which uses the interference pattern of waves, typically light waves, to measure very small distances, changes in length, or refractive index variations.
Which interferometers are there?
There are different interferometers with specific properties for different measurement tasks:
- Michelson-Interferometer measures the phase shift between two light beams. Michelson interferometers are commonly used in optical spectroscopy and astronomy.
- Mach-Zehnder-Interferometer allows the measurement of changes in the refractive index and is often used in telecommunications and environmental measurements.
- Fabry-Perot-Interferometer uses multiple interference between two parallel mirrors and is used in spectroscopy to measure wavelengths.
- fizeau-Interferometer measures distances and surface roughness, often used in materials science and in testing optical components.
- Sagnac-Interferometer is used to measure rotation and in fiber optics.
- Twyman Green-Interferometer is a variation of the Michelson interferometer, specifically for testing optical systems.
How does a laser interferometer work?
A pair of Laser interferometer acts as a beam splitter. It splits a laser beam into two parts that travel different paths and then merge again. These rays overlap each other and create an interference pattern that comes from the wave nature of light. If one of the paths changes e.g. B. due to a movement or a change in the refractive index, the interference pattern shifts. By analyzing this pattern change, these devices can make precise measurements of the measured variables distance, movement or optical properties.
How does interferometry work?
Interferometry is a measurement technique based on the principle of interference of waves, typically light waves. In interferometry, a wave is split into two or more parts that travel different paths and are then brought together again. When these waves come together, they overlap and form an interference pattern of light and dark stripes or rings. This pattern changes depending on the path differences between the waves caused by changes in length, movement, or differences in refractive index. By analyzing these pattern changes, one can make extremely precise measurements of distances, length changes, surface topographies and optical properties.
Where does interference take place?
Interference occurs when two or more waves - such as light, sound or water waves - meet and overlap. This happens in a variety of environments and situations, for example:
- During the optics: In the superposition of light waves in interferometers, in thin layers (like oil films on water), in soap bubbles and in the diffraction of light on gratings or slits.
- During the acoustics: When sound waves are superimposed, which can be observed in rooms with echoes or near speakers.
- During the Nature: When water waves are superimposed in bodies of water such as lakes or oceans.
Interference occurs when the crests and troughs of the superimposed waves come together in such a way that they strengthen each other (constructive interference) or weaken each other (destructive interference). The resulting interference patterns provide important information about the properties of the waves and the media through which they travel.
Source: This article is based on information from the following companies: Micro-Epsilon, Nortus-Optronic, Sios.
You might also be interested in...

Optimize weld seam with calculation and profile measurement

Distance sensors | Distance, path, distance & Co.

Accelerometer | Measuring forces and direction

Cable pull transmitter | Cable pull sensor and cable pull displacement sensor

Capacitive sensor for measurement under temperature fluctuations

Optical sensors | Light scanner, lidar sensor, laser sensor

Angela Struck is editor-in-chief of the development scout and freelance journalist as well as managing director of Presse Service Büro GbR in Ried.
