Smart robot software for processes with tolerances
- Details
- Hits: 856
If you try the traditional approach, processes subject to tolerance This is often a big challenge to automate. With the smart one robot software from Artiminds Robotics Reliable solutions can be created very easily. Various implemented examples illustrate the wide range of applications.
Contents
What characterizes processes with a high degree of tolerance?
Tolerance-affected processes in industry include, for example, the assembly of assemblies with cumulative tolerances, the handling of slack parts or end-of-line tests of complete assemblies.
Production processes in the areas mentioned usually have tolerances in several dimensions on. Here, the use of simple measuring methods or mechanical systems is not enough to reliably implement such automation tasks. There are often no software robot providers available on the market who are familiar with the development of special solutions with more complex measuring methods. Despite a sensible ROI, automation potential often remains untapped as a consequence.
With the smart ones software solutions Artiminds can meet the requirements of tolerance-based processes. Neither multidimensional tolerances are a problem, nor is a lack of expert knowledge.
Two steps lead to success here:
- The uncomplicatede Determination of the relevant tolerances: Various sensor methods can be used to measure the tolerances using the tools.
- The data drivene Improving the automation system increases performance because measured tolerances are reused.
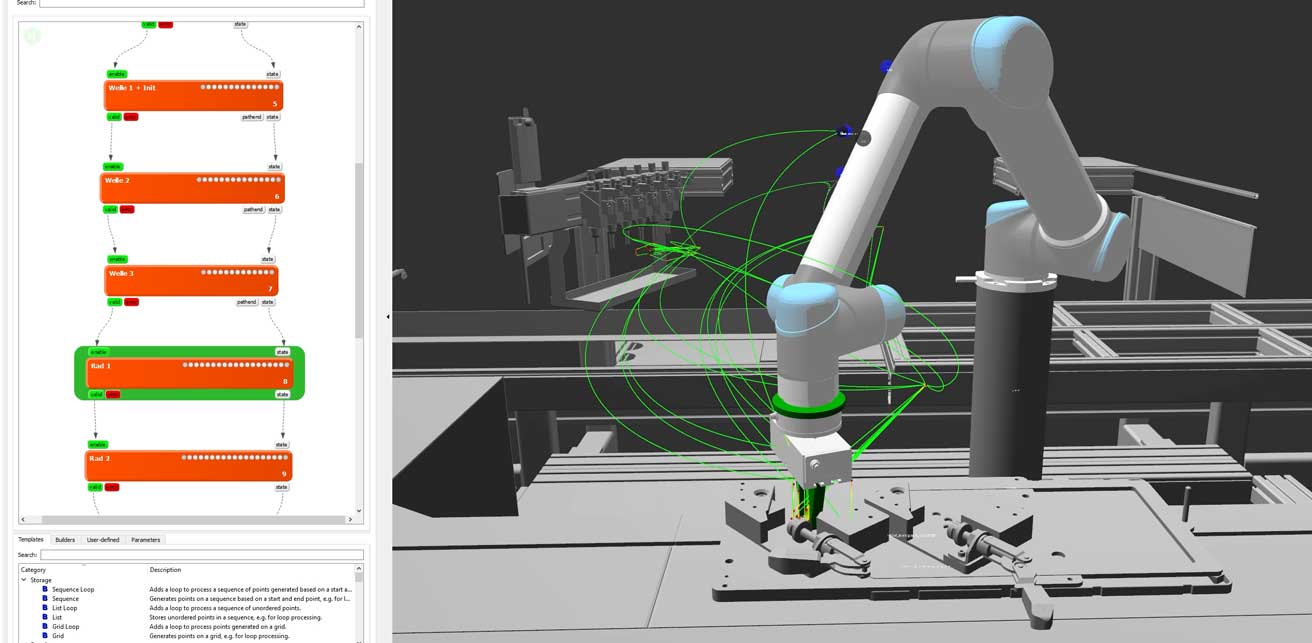
Three case studies
Plug assembly at EBM-Papst

EBM-Papst has been using three in the production of blower fans at the Landshut plant since the middle of last year Robotic-Solutions with the software from Artiminds. The application: Assembly robots attach circuit boards to a floating housing. The process, which is subject to high tolerances, is carried out reliably and in accordance with the cycle time using the features for tolerance compensation with the help of force/torque sensors.
For commissioning, the automatic recording and analysis of the Process data the results of individual tolerance compensation workpiece carriers assigned and then specifically improved. Other process steps in the system also benefited from this.
After assembly, two robots guide one End-of-line test through. There will be several Plug automatically contacted on the mounted, floating circuit board. Tolerance compensation is also carried out using the tools from Artiminds. This increases process reliability. The connector position on the circuit board is freely configurable. Therefore, in addition to different component variants, the robots have to cover up to 360 angular positions of the connector.
Teach point optimization for optimal cycle time
About the software function Teach point optimization (TPO) the cycle time requirements can be met. The appropriate approach point can be determined based on the previously carried out tolerance compensation for each variant and angular position. Over a SPS this is transmitted to the robot.
The process automatically adapts to the tolerances of the variants and angular positions after a few runs. Tolerances from additional batches can be integrated into the database during production. This Learning effect makes production more robust and prevents time-consuming re-teaching when conditions change.
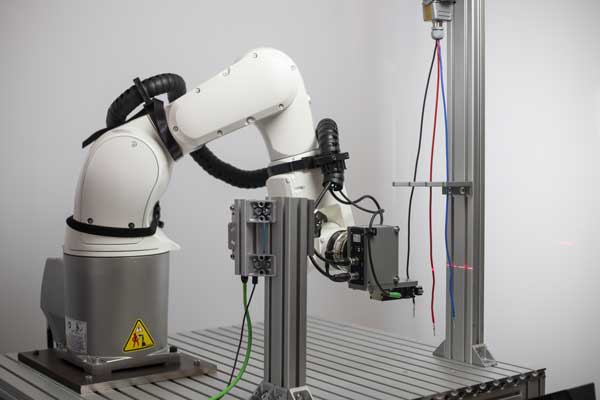
Cable handling with the block library
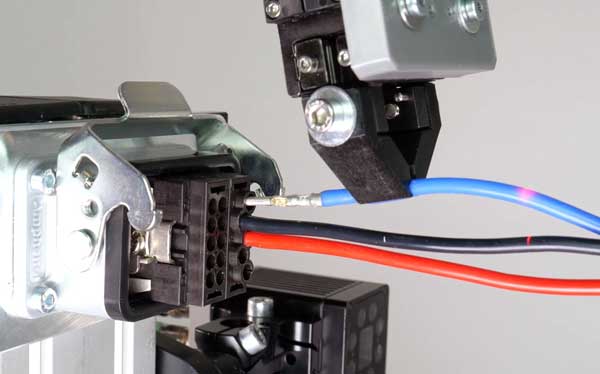
The automatic picking up of cables is a clear example of the challenges posed by flexible parts. About the Block library Artiminds allows you to adjust the grip point and orientation of the Gripper relative to Cables determine quickly and reliably. To do this, the end of the cable is scanned.
A wide range of feeding types can be realized in this way. To make implementing such an application as easy as possible, the software allows robots to easily use Standardsensors. 2D and 3D cameras or profile laser scanners that automatically determine and compensate for tolerances.
Calculate several measurements at the same time
However, in processes with high tolerances such as cable handling, not just one, but the same one often has to be used multiple measurements be offset to determine all tolerances. Profile laser scanners, which are comparatively easy to set up, measure the process along a line in three dimensions quickly, with high precision and cost-effectively.
Using the library, the results of Profile laser scanners further processed directly on the robot control without an additional evaluation computer. In addition to data reference (triggering detectors, result reference and multiple result storage), the library also supports data processing. This includes many possibilities for novel automation solutions - from simple operators such as security checks to more complex operators such as creating a scan from many measurements.
Force-controlled assembly at Primus Präzisionstechnik
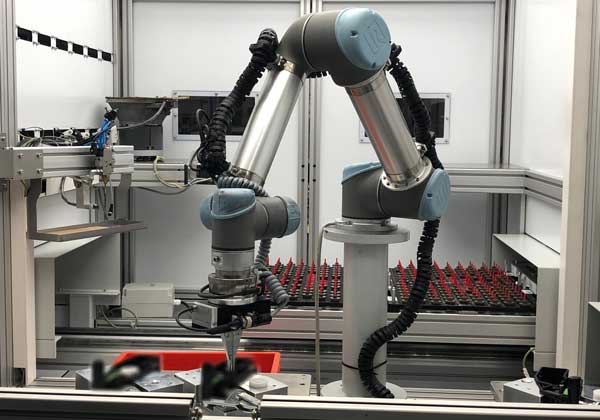

The analysis software LAR is a tool that can be used to obtain and save process data from the robot controller during ongoing operation. When assigned to the programmed sub-processes, their analysis and monitoring is easily possible. For processes with high tolerances, it is also worth going one step further:
With automatic TPO, data processing is standardized due to the interfaces used and access is easy. A variety of Filtering options is aviable. The user only decides how he wants to optimize: per workpiece carrier, workpiece variant or batch.
Automated gear assembly
The automatic assembly of gears Primus precision technology is a clear example: several individual parts become smalltransmission manufactured. There are three waves and five Gears to be installed in a gearbox housing. Before placement, all parts are greased. The application is complex, requires many process steps and different components, which results in a high number of variants.
For Primus, automation was about increasing the Process and repeat accuracy. LAR provides detailed evaluations and data about the production process based on robot movements, force/torque measurements, Image Processingresults or error codes. The potential for improvement cannot be seen with the naked eye, but it can be easily objectively assessed. As a result, the precision of the application can be readjusted down to the 100th range. After a few runs, you can evaluate again whether the changes have achieved the desired positive effect.
Conclusion
The three applications show that the tools from Artiminds without expert knowledge of people and without much programming effort, even processes with high tolerances can be automated in an economically sensible way. Due to the central use of the tools and standard components, the resulting system concepts are very flexible and easily adaptable to new requirements.
Artiminds Robotics exhibits at the following spring trade fairs: All about automation, booth B2-150 and Hannover Messe, Hall 5, Stand B28-11.

Silke Glasstetter is Head of Marketing at
Artiminds Robotics GmbH in Karlsruhe.
