Control and teaching box for robot programming
- Details
- Hits: 5764
The fast industrial and collaborative Melfa robots from Mitsubishi Electric are high precision, have intelligent technology and can be used in manufacturing cells. But the automation company also continually presents new developments in the area of software for robot programming, including one Teaching box and a platform that Robot programming and CNC combined.

Contents
Teaching box for faster use of robots
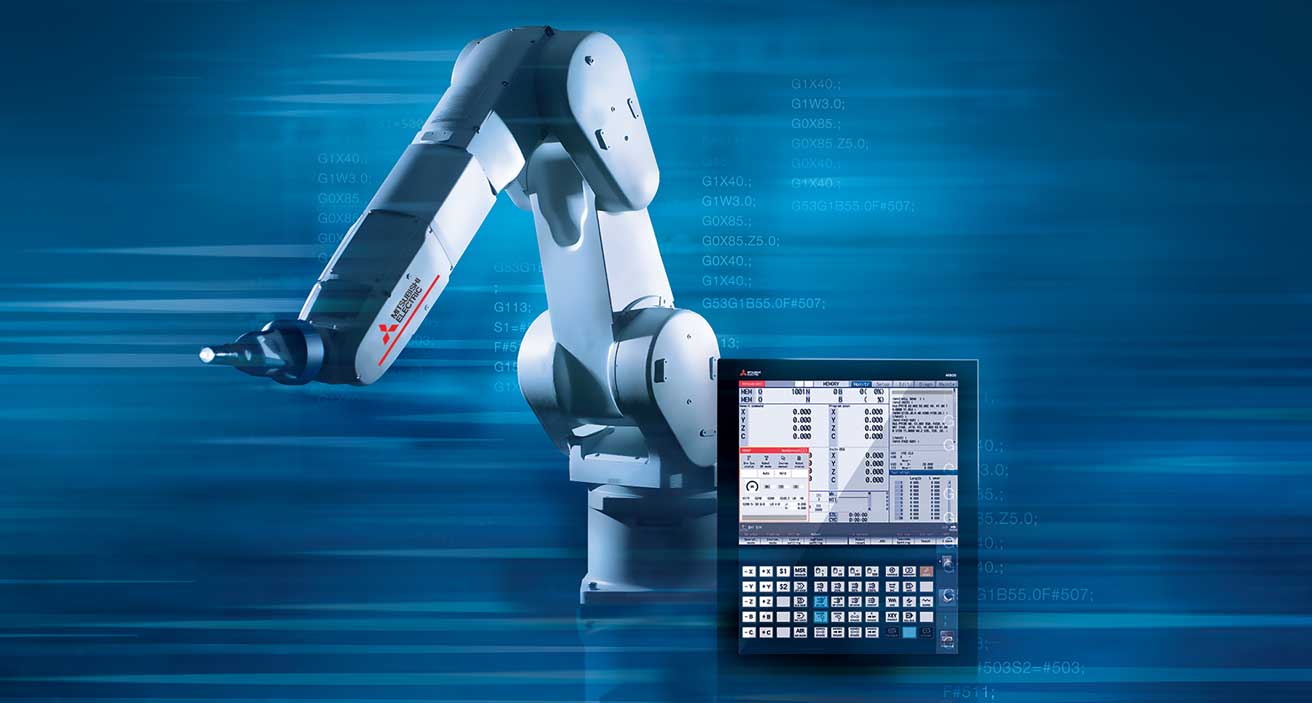
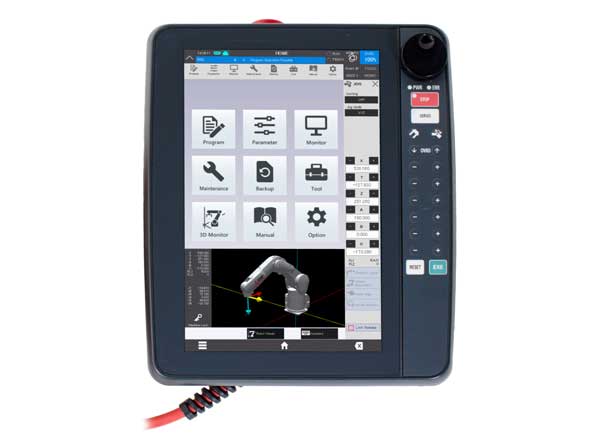 31.01.2024/XNUMX/XNUMX | Mitsubishi Electric brings with it R86TB a powerful teaching box onto the market. With it, users can set up, program, convert, maintain and troubleshoot industrial and collaborative Melfa robots. This simplifies the interaction between humans and machines and makes automated processes highly efficient.
31.01.2024/XNUMX/XNUMX | Mitsubishi Electric brings with it R86TB a powerful teaching box onto the market. With it, users can set up, program, convert, maintain and troubleshoot industrial and collaborative Melfa robots. This simplifies the interaction between humans and machines and makes automated processes highly efficient.
The multifunctional operating and programming panel is based on the proven teaching boxes from Mitsubishi Electric. The platform offers cost-effective, intuitive control for Melfa robot with advanced functions for monitoring and programming all generations.
The comprehensive one steering of the connected robot takes place via various screen masks using a high-resolution 10,1-inch display. In particular, the R86TB has 3D visualization capabilities.
These help system integrators, machine builders and end users plan, set up and program robotic tasks in an environment. The function is supplemented by parameter input, programming support, programming interfaces and a diagnostic area.
All functions are based on the manufacturer's own robot engineering software RT Toolbox3. This compatibility facilitates user acceptance of the use of these platforms.
The Teachingbox R86TB supports optimized uptime of automated applications as well as quick troubleshooting without a computer. The box was designed as the optimal interface for effortless interaction with Melfa robots during their entire lifespan
CNC + robot programming on one platform
The merger of Robotic and CNC Technology brings clear competitive advantages for machine builders and OEMs when designing CNC machining centers. By integrating the robot into the machine tool, the advantages of automation can be fully exploited and productivity increased. With the development of a unified programming environment, Mitsubishi Electric is creating a direct robot control system with which robot programming can be carried out via G-codes in the CNC machining center.
Robotics and CNC machining are two good examples of the declining half-life of State of the art technology. While CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology goes back to the programming of machines with punch cards in the 1950s, today's CNC machines can be used for multi-axis, fully automatic and computer-controlled machining and milling. The need for operators has grown rapidly. The Institute of Technical Trades US already claimed in 2016 that in many industries up to 40% of jobs would be needed in the field of CNC technology in the next few years.
The history of industrial robots

The first Industrial robots were developed in the late 1950s. Unimation's Unimate was the first commercial one in 1961 Industrial robots, who lifted and stacked hot metal parts on a General Motors assembly line in New Jersey, USA. In 1969, Stanford University introduced the first all-electric 6-axis articulated robot. It consisted of a combination of rotary, revolute, prism and ball joints.
In the 1970s were the first robotic arms developed for further automation: the Puma arms (Programmable Universal Machine for Assembly) equipped only with swivel joints increased the mobility of the arm. At the same time, elementary data processing was introduced to control arm position.
 Cobots as a door opener to the establishment of robotics in factory automation
Cobots as a door opener to the establishment of robotics in factory automation
The 1980s brought a new approach to robotics: The University of Yamanashi in Japan started with the Robotic technology Scale (Selective Compliance Articulated Robot) pioneered. The arm had only 4 joints and can only move in the three directions X, Y and Z. Even if it is considered "selectively compliant", it still offers advantages in terms of speed, space requirements and price compared to the more complex 6-axis robotic arms. One of the companies that brought this technology to market was Mitsubishi Electric. A compact 6-axis robotics followed shortly thereafter, offering more flexibility in complex assembly processes.
Mitsubishi Electric has continued this engineering over the past 40 years with the development of approx. 14 different generations continued on robotic arms. One of the major advances in automation was the reduction in robot cycle times. If you compare a robot from 1998 with a modern model, today's version is six times faster. Comparatively, the speeds of the fastest automobiles have only increased 1,4 times over the same period, reports Auto Express.
Not only has the basic speed of the robot arms improved, but the intelligent robot control also allows smooth movements and high acceleration. the cycle times improve drastically.
 ESD certified robots for handling electrical components
ESD certified robots for handling electrical components
The number of Mitsubishi Electric robot models has also increased. Originally it was less than 10. Today the automator has over 160 different versions with special features and modules in the portfolio, all tailored to the requirements of the industry. For example, special coatings are used for applications in the food and beverage industry. Or special seals make the robot suitable for clean rooms.
A lot has also happened in terms of security. Originally, industrial robots required fixed guards. Today they are equipped with security interfaces that no longer make this necessary. When Cobots they can even work closely with humans. The new Melfa Assista sets new standards in the modern production process.
Advances in robot programming
The advent of computers made CNC machines more powerful and advances in robot programming changed robot applications. Early designs were based on digital signals as the interface between the robot and the machine controller. Today, robots and programmable logic controller (PLC) of the machine into a platform. This increases the amount of data to be transferred and the speed of data transfer.
This availability of data opens up new opportunities to increase plant productivity and returns. Information about the performance and runtime of individual components within the robot is predictive maintenance used. This avoids machine downtime and reduces downtime. If the data is transferred to a cloud, robots at different locations can be managed or compared. This allows users to see how they behave.
Peripheral technologies have also been further developed. So recognize Sensors at the end of a robot arm, the force exerted and give feedback to the robot controller when, for example, a robot inserts one part into another. the steering the optimal force improves the quality of the workpieces. Also sensors for Image Processing have become commonplace in industrial robs. They can be used to guide the robot to the desired position. It is important that such sensors or cameras can be easily and practically integrated and programmed.
 Robot programming for automated THT assembly
Robot programming for automated THT assembly
But perhaps the most important engineering development has been in the field of Software completed for robot programming. Software tools simplify the robot programming process, even for highly complex tasks. Because they allow the complete simulation of the systems. Bad hardware purchases can thus be safely ruled out in advance. This gives developers and customers the guarantee that a system will work as planned. As with the drag & drop software for robot programming RT-Visualbox, the interface is becoming more and more user-friendly.
Software development is at the heart of the latest innovation: Self-directed robots use sensors to scan their surroundings and plan their movement to avoid obstacles - in real time. Even when multiple people and robots like cobots work in the same space, robots can work without supervision.
Robot control combines CNC with robotics

In order to increase the overall throughput significantly, robot technology has been strengthened in recent years machine loading used for efficient loading and unloading of machining centers. This shortens cycle times and increases the efficiency of the entire production process. In this way, larger batches can run independently overnight.
So far, however, there has been a major challenge: The programming language of modern robots differs greatly from the programming language G-Code, which is used when programming CNC controls is applied. A machining center can be quickly set up by programming G codes. However, this speed advantage was lost if the machine operator also had to learn the script-based programming language for robots. With the new robot controller Direct robot control Mitsubishi Electric has brought together the previously separate automation technologies for its Melfa robot family.
With this direct robot control, the robot control and PLC of the CNC machine are no longer programmed separately. Rather, the robot lets itself over G codes program in the CNC machining center yourself. So it is considered part of the processing order. It can even be moved with the hand wheel of the machine. Warnings or alarms from the CNC and robot are also recorded in the same log.
The new robot control opens up new possibilities. companies need in times of skills shortages only a specialist and original equipment manufacturer can more easily integrate robotics into their CNC machine.
In the last 50 years, robotics and CNC machining have developed massively. The present will continue to deepen this in the future. technologies like Artificial intelligence will find its way into the automation components and machine learning will make the robotic machining center more efficient. Mitsubishi Electric is leading the way with its proprietary Maisart AI technology.
Cooperation Robot Ready with Kuka – video
You might also be interested in...

Artificial Intelligence | trends and developments

Predictive maintenance for robotics, machines and systems

Mitsubishi Electric | Automating the World

Cobot | Discover collaborative robots as a new employee

battery production | Facts and Technologies

