for additive manufacturing
3D printing process, 3D printer, filament or printing material, etc. for modern mechanical engineering and special industries
Image: Fraunhofer IWU
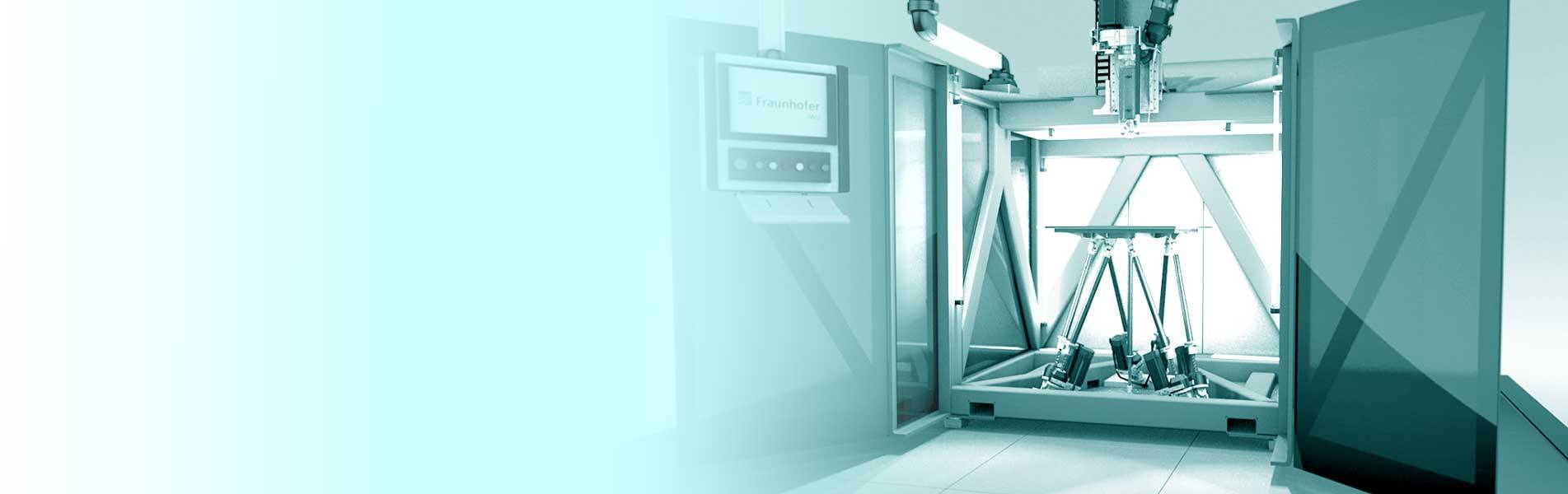

for additive manufacturing
3D printing process, 3D printer, filament or printing material, etc. for modern mechanical engineering and special industries
Image: Fraunhofer IWU
There are some names for the 3D pressure such as additive manufacturing, generative manufacturing or rapid prototyping. after that 3D Printing process initially found its way into prototype production, is now well on the way to mass production. Here you will find a wide variety of 3D printing innovations such as 3D printing processes, -printer, Filaments or Materials etc. for modern mechanical engineering and special industries.

Find out about news from the up-and-coming 3D printing technology or the additive manufacturing processes. Here you will find components made of plastic or metal, processes such as selective laser sintering (SLS) or stereolithography (SL) and 3D printers from Igus, Schaeffler, Systec or Voxeljet, among others. Don't miss any industry firsts for shaping your structural components.











Whether additive manufacturing, generative manufacturing or rapid prototyping, components are manufactured in these processes on a 3D printer. Now these are Printing process arrived a little further in the industry and is therefore also suitable for series and mass production. Here we present innovations and applications of the 3D printer for plastics before:
The metal 3D printer is being used more and more in production. Instead of waiting days or weeks for traditional processing, metal parts now almost immediately in hours and without extra Tools 3D print. Precision parts and assemblies can be manufactured quickly and inexpensively. The article presents novelties and applications of additive manufacturing for Metals before like the first steel engine in just one component.
The filaments and materials fAdditive manufacturing is constantly evolving. The current development status for material for 3D printing processes shows a increasing diversity and higher productivity 3D printer Materials that not least meet the often robust requirements in industry. In addition to sustainability, the components must also be increasingly high-performing. In this article you will find out what is available and where the journey is going.
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, encompasses a variety of manufacturing processes, all based on the same fundamental concept: building an object layer by layer. These include techniques such as stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), Selective Laser Melting (SLM), fused deposition modeling (FDM), and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (Dmls), to name just a few. You can find out what is behind the individual procedures here.




There are a number of leading companies in the 3D printing industry that specialize in the manufacture of 3D printers, components and filaments. Some of them are:
Igus is a manufacturer of specialty filaments for 3D printers, particularly those designed for moving applications. The company also offers a comprehensive 3D printing service.
Igus has been building the division for a few years additive manufacturing with 3D printing, filament development & Co. Brand new is a new service life calculator for 3D printed parts, which calculates wear-resistant and smudge-free parts online in just 30 seconds. and there is a 3D printing service for XXL parts up to 3 m in size. With 4K for 3D, the Cologne company offers one Multi-material printing for multifunctional components. You can find this and all other innovations in additive manufacturing at igus here.
3D printers at igus also produce components with different filaments. In the 2-component 3D printingprocess, various material properties can be easily combined. So e.g. B. components gain a special rigidity and high wear resistance. The latest new development is the igus 3D printing filament Igumid P190. A carbon fiber reinforcement makes it extremely stiff and strong. The article introduces you to these and other new developments.
The special machine construction of the Schaeffler Group, Special Machinery, provides equipment for additive manufacturing, including multi-material 3D printing systems for unique material combinations.
The Schaeffler Group presented at the Automatica 2023 a novel system for additive manufacturing for industry. The multi material 3D printer offers a limitless potential for unique material combinations and functional integration, free design creation and fast market reactions in additive manufacturing.
Additive manufacturing has revolutionized numerous industries by speeding up the production of prototypes, one-offs and short runs and reducing costs. Here are some of the industries where 3D printing is particularly popular:
Let's take a closer look at the following applications:





The history of 3D printing began in the 1980er years ago, when Hideo Kodama of the Nagoya Municipal Industrial Research Institute filed the first patent for a rapid prototyping system. Shortly thereafter, in 1986, US engineer Chuck Hull founded 3D Systems and developed stereolithography (SLA). Mr. Hull is also credited with inventing the STL file format, which is still widely used today.
In the 1990er Over the years, other 3D printing technologies have been introduced, such as fused deposition modeling (FDM) by Scott Crump, who later founded Stratasys, and selective laser sintering (SLS) by Carl Deckard at the University of Texas. These technologies have greatly expanded the possibilities of additive manufacturing and led to its increasing use in prototyping, model making, and tooling.
In the 2000er Over the past few years, additive manufacturing has become increasingly widespread, particularly with the advent of desktop 3D printers. In 2005, the Reprap project started with the goal of creating self-replicating printers. This led to a proliferation of open source 3D printing technologies. In the decade that followed, companies like Makerbot and Ultimaker introduced affordable desktop 3D printers, making 3D printing accessible for home use and small businesses, such as printing spare parts.
Today, the 3D printing process is used in a variety of industries such as medical technology, the automotive industry and aerospace.
According to the Wohlers Report, overall global growth in additive manufacturing is increasing 2023 by 18,3%. According to Million Insights market report, the global 3D printing market will be worth USD 2030 billion by 76,17. According to Fortune Business Insights, the global 3D printing market was worth US$2022 billion in 18,33 and is expected to reach US$2030 billion by 105,99.
Additive manufacturing has made significant advances in recent years. Here are some of the most important trends for 2023:
3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that creates three-dimensional objects from digital models by adding material layer by layer until the desired design is achieved.
Sources: This article is based on information from the following companies: 3D Systems, ABB, BCN3D, Dr. Tretter, Fergal Coulter, Formlabs, Gimatic, Igus, Marting Luther University Halle-Wittenberg, Nanoscribe, Nexa 3D, Printsontes, PTC, Schaeffler, University of Würzburg, Voxeljet.