5G network | advantages and challenges
- Details
- Hits: 5652
Without communicating about that 5G network save Industry 4.0 or is the 4G network still sufficient? After all, 5G allows peak data rates of up to 10 Gbit / s, latency times of less than 1 ms, availability of over 99,999% and is also extremely energy-saving. HMS Industrial NetworkAs a verified partner of Ericsson the necessary hardware for that factory Automation.
Contents
More than just factory automation
With Router, Switch or Gateway from the manufacturer, the integration of 5G communication in systems and machines can be easily implemented and 4G can be replaced. However, the use cases for 5G technology go far beyond factory automation and there will be more and more in 2020.
Not so long ago was the popularity of wireless communication in industrial applications even smaller than the skepticism about it. Today we are certain that Industry 4.0 can only be implemented wirelessly. However, existing technologies often do not yet meet the requirements in the digital factory. There is a lack of bandwidth, reliability, capacity or real-time behavior.
 6G network | Bidirectional radio link and Thz receiver
6G network | Bidirectional radio link and Thz receiver
The 5G expansion promises a remedy here. Since November 2019, licenses for private campus networks can be applied for from the Federal Network Agency in Germany. Private 5G networks can also be used in France, Great Britain, the USA and Japan. But how do you actually apply for a local 5G campus network? How much does a 5G network actually cost? What is the status of infrastructure and hardware for 5G mobile communications technology? And last but not least: Who benefits from using the %G network anyway?
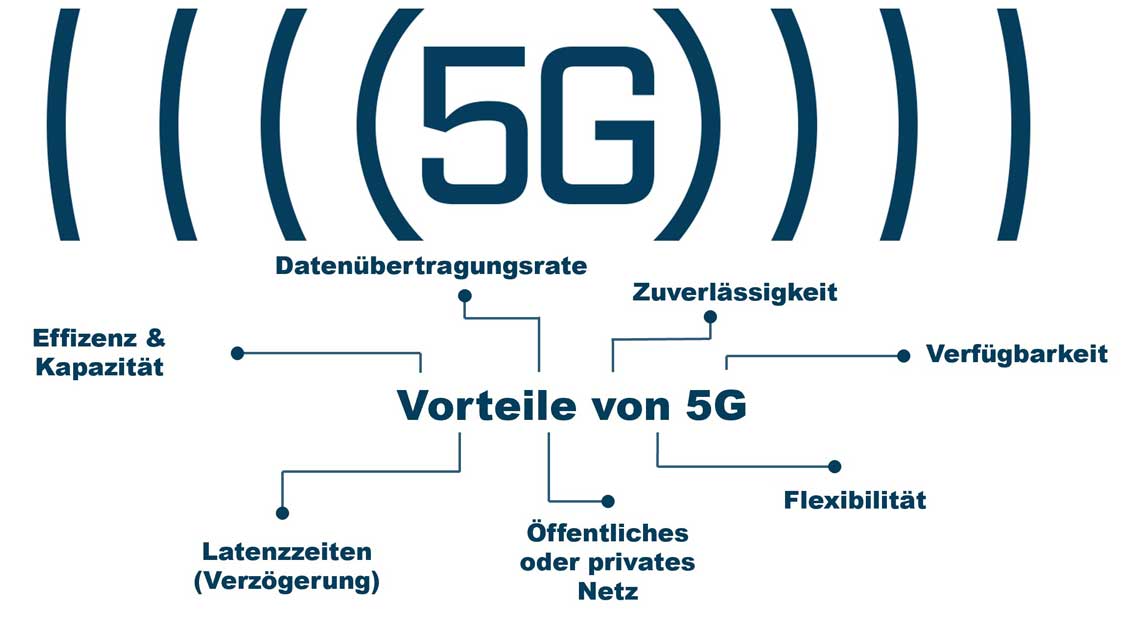
Advantages of 5G network in automation
 The mobile network standard 5G network expansion in the final stage for the automation industry is very promising. Gigantic data rates with minimal latency create the possibility for wireless real-time applications. Different profiles allow the optimal use of 5G in accordance with the application. Enhanced mobile broadband (EMBB) achieves peak data rates in excess of 10 Gbit/s. Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC) supports latency times under 1 ms with an availability of over 99,999%. Strictly speaking, that means half an hour of downtime in 10 years. With massive machine-type communication (MMTC) you can car's battery performanceoperated devices are operated for ten years. Up to one million devices per km² can be connected.
The mobile network standard 5G network expansion in the final stage for the automation industry is very promising. Gigantic data rates with minimal latency create the possibility for wireless real-time applications. Different profiles allow the optimal use of 5G in accordance with the application. Enhanced mobile broadband (EMBB) achieves peak data rates in excess of 10 Gbit/s. Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC) supports latency times under 1 ms with an availability of over 99,999%. Strictly speaking, that means half an hour of downtime in 10 years. With massive machine-type communication (MMTC) you can car's battery performanceoperated devices are operated for ten years. Up to one million devices per km² can be connected.
With the right license from the network operator, companies can now use all of these advantages on their own premises in the private 5G network. These campus networks create the conditions for the smart factory of the future. The skepticism associated with the use of a third-party network finally disappears with the private network.
What does a 5G network cost?
 Since November 21.11.2019, 5, 5G frequencies can be applied for for local applications. The application forms are available on the website of the Federal Network Agency. The costs are essentially made up of the one-off costs for the allocation of the 5G frequencies, ongoing usage fees for the frequencies, planning and setting up the infrastructure for communication with hardware, maintenance and operation of the XNUMXG technology. The one-off fee from the network operator for the allocation of frequencies is calculated using the following formula:
Since November 21.11.2019, 5, 5G frequencies can be applied for for local applications. The application forms are available on the website of the Federal Network Agency. The costs are essentially made up of the one-off costs for the allocation of the 5G frequencies, ongoing usage fees for the frequencies, planning and setting up the infrastructure for communication with hardware, maintenance and operation of the XNUMXG technology. The one-off fee from the network operator for the allocation of frequencies is calculated using the following formula:
License fee = 1000 + B x t x 5 x (6 x a1 + a2)
The formula contains the requested bandwidth B (between 10 and 100 MHz), the period t for which the frequency is requested and the area a in km² on which the private network is to be used. Allocation areas on settlement and traffic areas, i.e. densely populated and Industrial areas fall under a1 and must be calculated with a factor of 6. Other areas fall under the factor a2, for which there is no multiplier due to the much larger areas. This makes the purchase attractive for agriculture and forestry, for example. An operating area of 0,5 km² in a settlement and traffic area of 100 MHz for a period of five years therefore costs a one-time fee of 8500 euros (1000 + 100 x 5 x 5 x (6 x 0,5 + 0)).
 Energy efficient radio network for AGVS in intralogistics
Energy efficient radio network for AGVS in intralogistics
There are also ongoing Frequency usage fees. They consist of usage fees for the frequencies in accordance with Section 143 (1) TKG (Telecommunications Act), Section 35 FUAG (Law on the Provision of Radio Systems on the Market) and contributions in accordance with Section 31 EMVG (Law on Electromagnetic Compatibility). These fees apply retrospectively for one year. The amount is based on the applicable frequency protection fee regulation. So far, values from similar user groups from the previous year have been used as a guide.
There are also costs for planning, purchasing and setting up your own infrastructure, which essentially depend on the respective application and size of the campus. As with the operation of wired networks, also plan costs for maintaining the network.
Planning and hardware for private 5G cellular standard
Planning companies and system integrators support users in planning private campus networks. Among other things, they determine the real needs, help with the application process, ensure that the network meets the requirements of the Federal Network Agency and take care of the practical structure. The Swedish company Ericsson, which focuses on cellular technology, Internet and multimedia communication and teleeffective communication has been dealing with the topic of private campus networks based on 5G for some time.
 Gateways for Industry 4.0 factory networks
Gateways for Industry 4.0 factory networks
It has set up a partner portal to support interested companies. These partners help build the communication infrastructure on the company premises and implement 5G communication for the individual machines and systems.
Certified partner for communication in factory automation
 HMS Industrial Networks is a certified partner for products for communication in the field factory Automation. The company supports machine builders with advice and suitable components to make 5G technology integration as easy as possible for them.
HMS Industrial Networks is a certified partner for products for communication in the field factory Automation. The company supports machine builders with advice and suitable components to make 5G technology integration as easy as possible for them.
The Anybus wireless router for example, are powerful and reliable with greater mobility and low latency for wireless networks. They are currently available for LTE and WLAN, and a variant of 5G networks is being planned. The HMS Wireless Bolt, a radio, is currently in the proof-of-concept phase Gateway for direct machine access via 4G/5G. The same applies to switches with which machines can be connected directly to the 5G network.
Bridges for wireless Profinet and Profisafe use via the 5G network are also in the pipeline. These solutions are of interest to companies who want to make existing systems fit for the future and those who rely on future-oriented communication technology to build new locations.
5G network benefits in practice
 The factory Automation with driverless transport systems and modular, flexible work cells is a classic application for the 5G network. In the future, however, many other areas will also benefit from the 5G mobile network thanks to the cost structure for the license allocation.
The factory Automation with driverless transport systems and modular, flexible work cells is a classic application for the 5G network. In the future, however, many other areas will also benefit from the 5G mobile network thanks to the cost structure for the license allocation.
So in the future Agriculture and Forestry When transferring their data, rely on modern technologies that were previously unusable. This applies to animal husbandry and milk production, among other things. In arable farming, a lot of information about sowing and harvesting can be determined with the 5G network expansion in connection with precision farming and this can be optimized for further cultivation. From the data you can e.g. B. deduce how much fertilizer may be applied where. Likewise, the use autonomous vehicles possible. And so the private campus networks will not only be beneficial for farmers, but also for animal welfare and environmental protection.
 Also in container ports there are lucrative applications. Countless goods are handled on huge sites. The resulting data volumes exceed the capacity of previous wireless networks. Using the 5G cellular standard, cranes, containers, vehicles and employees can communicate wirelessly, reliably and securely with one another. The same applies to airports and the apron vehicles used there.
Also in container ports there are lucrative applications. Countless goods are handled on huge sites. The resulting data volumes exceed the capacity of previous wireless networks. Using the 5G cellular standard, cranes, containers, vehicles and employees can communicate wirelessly, reliably and securely with one another. The same applies to airports and the apron vehicles used there.
Of course it also offers process industry a variety of applications. Just think of the large premises of oil refineries or chemical parks. You benefit from the fact that the 5G standard is a universal communication medium for indoor and outdoor applications.
Basically, 5G technology works in applications in which many sensors deliver such large amounts of data that it has not yet been possible to transmit them wirelessly, but in which the flexibility of wireless communication is wanted. Certainly not all cables will disappear from the digital factory in the long term. Which will still be left in a few years, companies will have to clarify individually depending on their application.
 EKS Angels | The fiber optic specialists
EKS Angels | The fiber optic specialists
