Connectors for medical devices and wearables
- Details
- Hits: 7676
Fischer connectors presents its smart Connection Technology for electronic Medical devices and Wearables. Connectors are very robust, reliable, easy to operate and clean and easy to integrate, especially for medical applications. The Plug can be installed, for example, in surgical instruments, diagnostic devices, dental and therapeutic equipment, heart support systems and disposable devices.
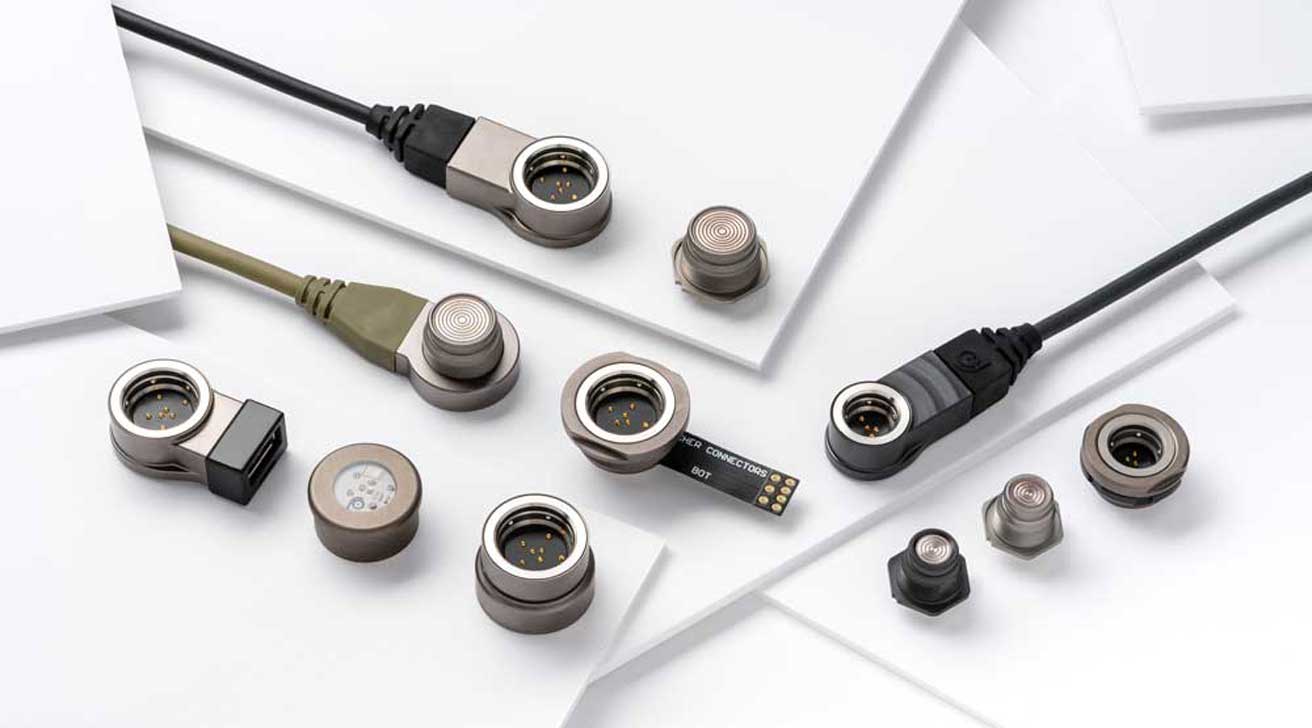

Here they secure their power and data supply. They are also used in Patient monitoring systems or exoskeletons. The extensive product range includes fully sterilizable and reusable connections and hybrid connectors. The highlights of the trade fair presence are the connectors and active components from the Fischer Freedom series.
 Adaptive exoskeleton for the stroke patient
Adaptive exoskeleton for the stroke patient
These robust, small plug connections optimize cable management with their 360-degree plug-in option. They help development engineers to implement more flexibility in technology and user comfort in fixed, mobile and wearable medical devices and wearables.
Connectors for networking in medical technology
"Networking is an important trend in all areas of medicine, from the operating room to small smart monitoring devices directly on the patient," knows Martin Wimmers, Managing Director of Fischer Connectors GmbH. "If health is at stake, proven and reliable components and connection technology as well as a high level of user convenience are also indispensable, even with the connectors. We therefore work closely with developers and providers of medical technology to ensure optimal power and data supply with connectors for every application. ”
Fishermen's plugs Freedom series are characterized by their plug-and-use technology. They can be blind plugged in 360 degrees. So they can be placed anywhere where conventional Connectors are unsuitable. As a result, medical connectors are used for numerous applications in the areas of surgery, intervention, diagnostics, imaging, as well as monitoring and therapeutics. Fischer also shows the active components of the series: USB 2.0 adapter, LED connector and robust flash drive.
Overview of medical technology connectors
You might also be interested in...