Embedded heatpipes improve the heat dissipation of circuit boards
- Details
- Hits: 5229
 The service life of electronic components can be drastically reduced by increasing the operating temperature by just a few degrees Celsius. In addition, heat dissipation is made more difficult by the fact that the entire circuit board is encapsulated in certain applications in order to protect it effectively from moisture and dust. Embedded and inserted heat pipes from AT + S significantly improve heat dissipation.
The service life of electronic components can be drastically reduced by increasing the operating temperature by just a few degrees Celsius. In addition, heat dissipation is made more difficult by the fact that the entire circuit board is encapsulated in certain applications in order to protect it effectively from moisture and dust. Embedded and inserted heat pipes from AT + S significantly improve heat dissipation.
Modern thermal management of printed circuit boards is essentially accomplished by adding additional copper to the printed circuit board through design measures such as thick copper layers, plated-through holes, laser-drilled copper fill vias or even copper inlays. Although these methods can provide good heat dissipation, they also suffer from several disadvantages for various reasons. Especially in the case of thick copper layers, which dissipate heat, the production of printed circuit boards becomes more expensive and more difficult because of new equipment for handling the heavy ones , thick copper plates are necessary.
Save weight
In addition, high-density packaging requires extremely narrow copper tracks in the circuits of printed circuit boards. This is not so easy to do when thick copper layers have to be etched. In aerospace applications, mass also plays an important role and is also becoming increasingly important in modern automobiles such as electric vehicles. In addition, larger amounts of copper used for cooling can become very expensive. Thermal management concepts such as modern miniaturized heatpipes, which are lightweight, offer better thermal conductivity than copper, and are suitable for PCBs due to their small size, can solve the thermal management challenges of today's high-end applications.
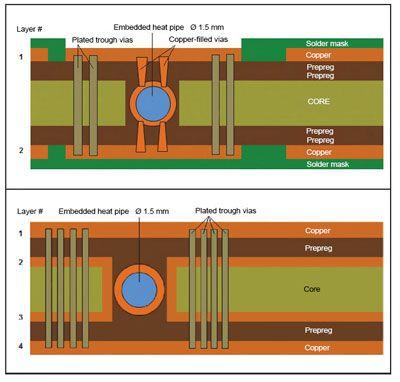
Because of their superior heat transfer capability at a relatively low mass, heat pipes can conduct heat very effectively through the circuit boards. Modern heat pipes are so small that they can be integrated into circuit board constructions. Their thickness is in the range from about 400 µm to 2 mm. The manufacturer uses the company's own know-how in embedding components and in 2.5D technology to connect mini heat pipes to circuit boards.
New design options
The use of heatpipes directly in the PCB allows new design options such as external cooling and heat dissipation and dissipation. For example, heat dissipation offers the opportunity to use temperature-sensitive components such as sensors and MEMS in the immediate vicinity of heat-generating components such as transistors. In addition, the improved cooling characteristics of printed circuit boards with embedded heatpipes (HP-PCBs) allow devices to operate at lower temperatures, increasing efficiency, life, and energy savings in most electronic applications.
The embedded or inserted heat pipe is a passive component that can dissipate heat in the circuit board over longer distances, more effectively than conventional heat conductors such as copper. Their mechanism of heat dissipation is based on a phase transition (i.e. from liquid to gas) and the transport of mass.
How the heat pipe works
The heat pipe is a tubular construction that is tightly closed at both ends and contains a liquid in which there is a very low pressure. Usually the pipe is made of copper and the liquid used is water. When one end of the pipe is heated, the water changes from the liquid to the gaseous phase - in simple terms: it evaporates. The associated increase in pressure causes the water vapor to flow to the cold end of the pipe. There the steam gives off energy and becomes liquid again. The liquid water is transported back to the heated end of the pipe by capillary forces. This dynamic process repeats itself continuously and leads to a heat dissipation that is a hundred to several thousand times as high as with a piece of copper with corresponding dimensions. Because the heat pipe is hollow, it has the added benefit of being much lighter than copper rods.
In the concept presented, ready-to-use mini-heatpipes are connected to the PCB body, resulting in a complete thermal management module. Several printed circuit board demonstration samples with embedded and inserted heatpipes were produced. To connect the miniaturized heatpipes to the circuit board, various methods were used. In all experiments, the HP-PCB concept helped to improve the overall temperature behavior of the system compared to currently used methods. This technique is considered a thermal management concept for virtually all applications in electronics where better heat dissipation or dissipation is required. Possible areas of application are especially where restrictions in terms of mass and space requirements exist. Examples include aerospace, automotive, and modern server applications.
Partners wanted
The research and development department of AT + S is still looking for partners who have special requirements for the thermal management of future products and who are ready to test the HP PCB technology as a first-time user. The company's vision is that advanced PCBs must provide advanced capabilities such as improved thermal management, embedded components, high frequency, and hybrid materials as an integral part of the technological challenges of future applications.
